|
|
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
摘要:深度学习鲁棒蛋白质序列设计、超偶然随机初始化表现及如何找到它们、面向图像-语言和视频-语言任务的基础模型、能从2D视觉Transformer开始解决3D视觉任务吗、基于参数化专家的高效学习数据增强、深度学习低样本目标检测综述、分层Bregman表示学习及其知识蒸馏应用、少样本语言模型微调的冷启动数据选择、场景文本理解预训练
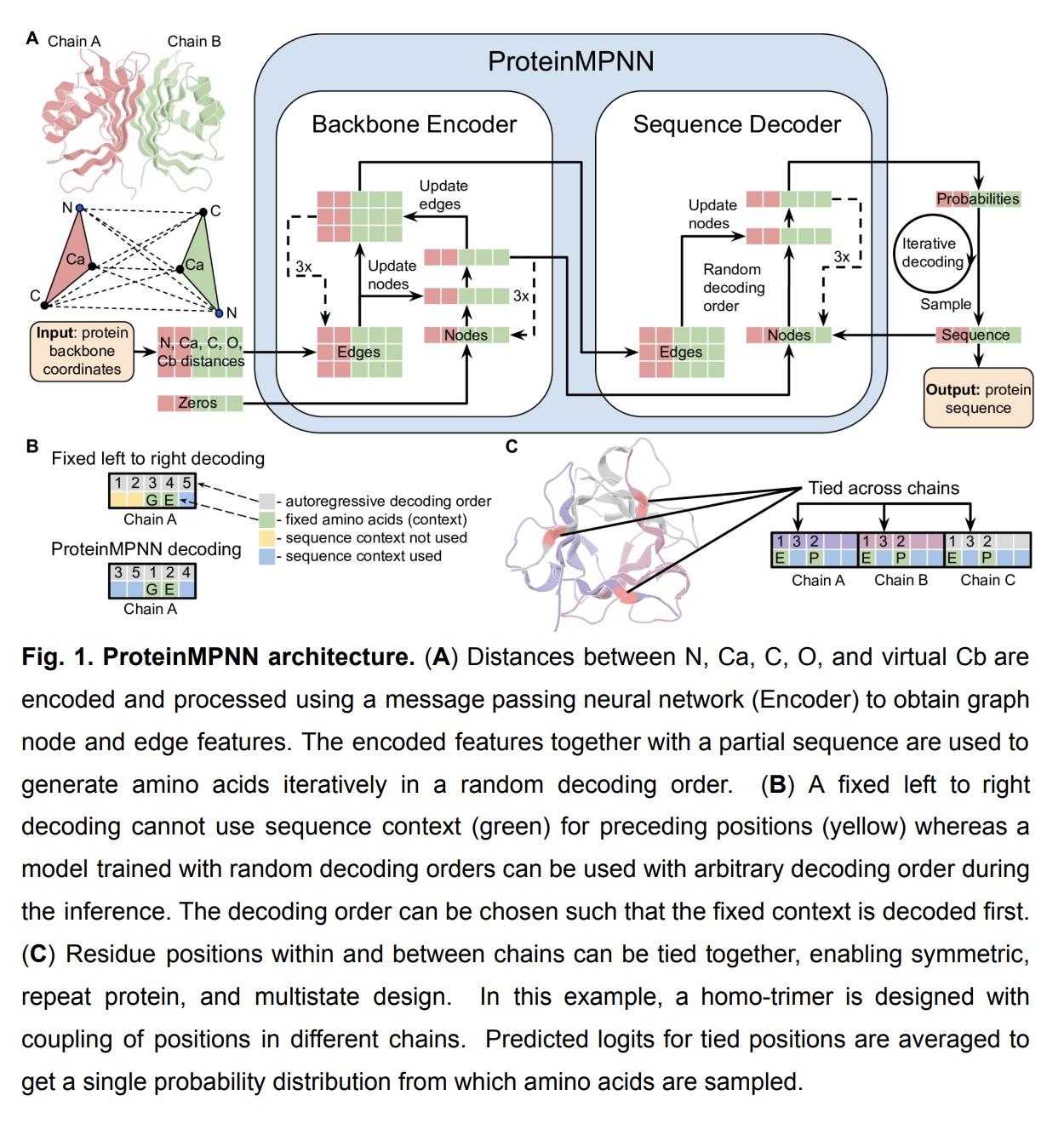
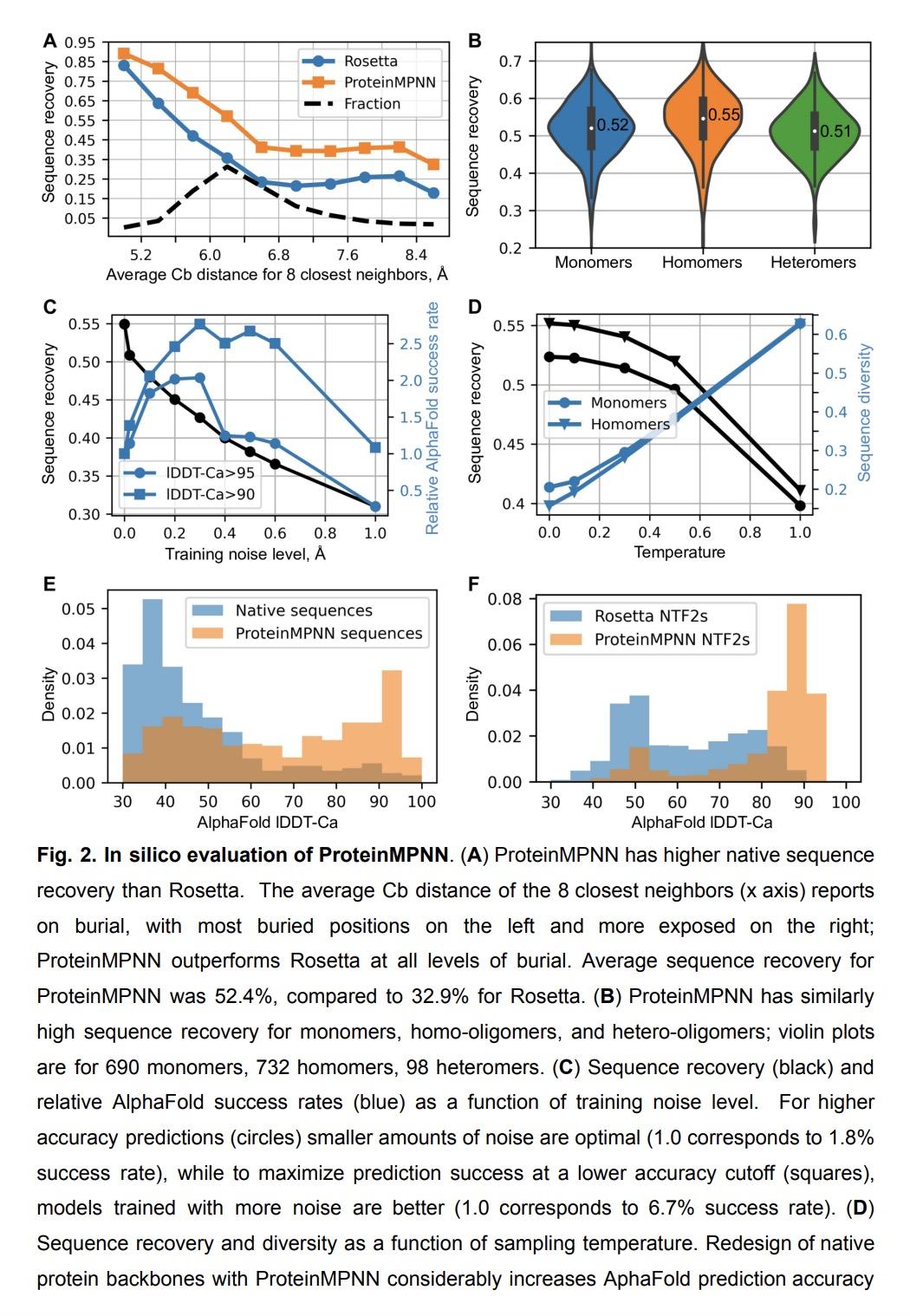
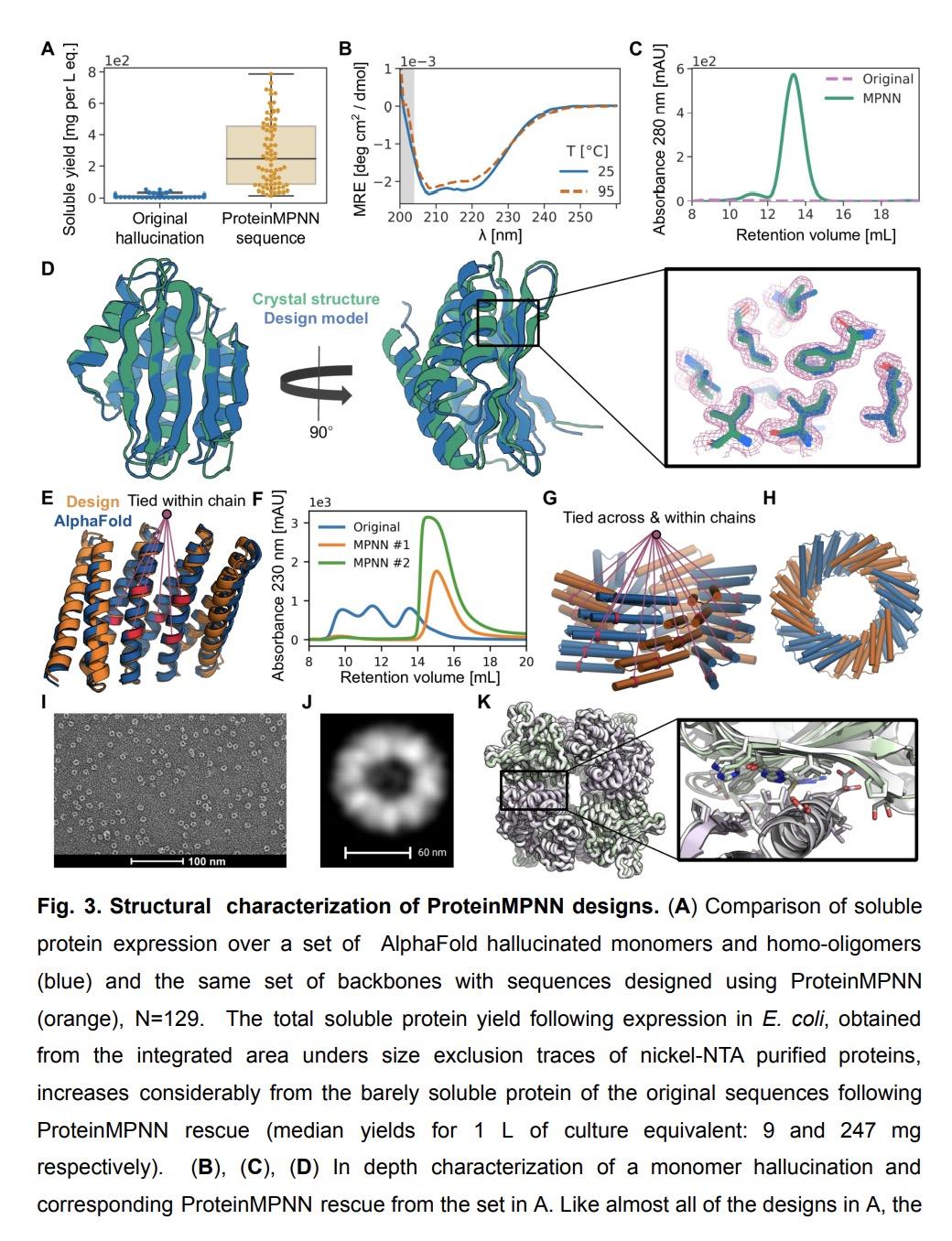
1、[LG] Robust deep learning based protein sequence design using ProteinMPNN
J Dauparas, I Anishchenko, N Bennett, H Bai...
[University of Washington & Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory]
ProteinMPNN深度学习鲁棒蛋白质序列设计。虽然深度学习已经彻底改变了蛋白质结构预测,但几乎所有的实验特征的新蛋白质设计都是用基于物理的方法产生的,如Rosetta。本文描述了一种基于深度学习的蛋白质序列设计方法,ProteinMPNN,在硅基和实验测试中都有出色的表现。不同位置的氨基酸序列可以在单链或多链之间进行组对,从而能应用于当前广泛的蛋白质设计挑战。在本地蛋白质骨架上,ProteinMPNN的序列恢复率为52.4%,而Rosetta为32.9%。在训练过程中加入噪声可以提高蛋白质结构模型的序列恢复率,并且产生的序列可以更鲁棒地编码它们的结构,这是用结构预测算法评估的。利用X射线晶体学、低温电镜和功能研究证明了ProteinMPNN的广泛实用性和高准确性,它挽救了以前用Rosetta或AlphaFold设计的失败的蛋白质单体、环状同源多聚体、四面体纳米颗粒和目标结合蛋白。
While deep learning has revolutionized protein structure prediction, almost all experimentally characterized de novo protein designs have been generated using physically based approaches such as Rosetta. Here we describe a deep learning based protein sequence design method, ProteinMPNN, with outstanding performance in both in silico and experimental tests. The amino acid sequence at different positions can be coupled between single or multiple chains, enabling application to a wide range of current protein design challenges. On native protein backbones, ProteinMPNN has a sequence recovery of 52.4%, compared to 32.9% for Rosetta. Incorporation of noise during training improves sequence recovery on protein structure models, and produces sequences which more robustly encode their structures as assessed using structure prediction algorithms. We demonstrate the broad utility and high accuracy of ProteinMPNN using X-ray crystallography, cryoEM and functional studies by rescuing previously failed designs, made using Rosetta or AlphaFold, of protein monomers, cyclic homo-oligomers, tetrahedral nanoparticles, and target binding proteins.
https://science.org/doi/10.1126/science.add2187
biorxiv: https://biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.06.03.494563v1

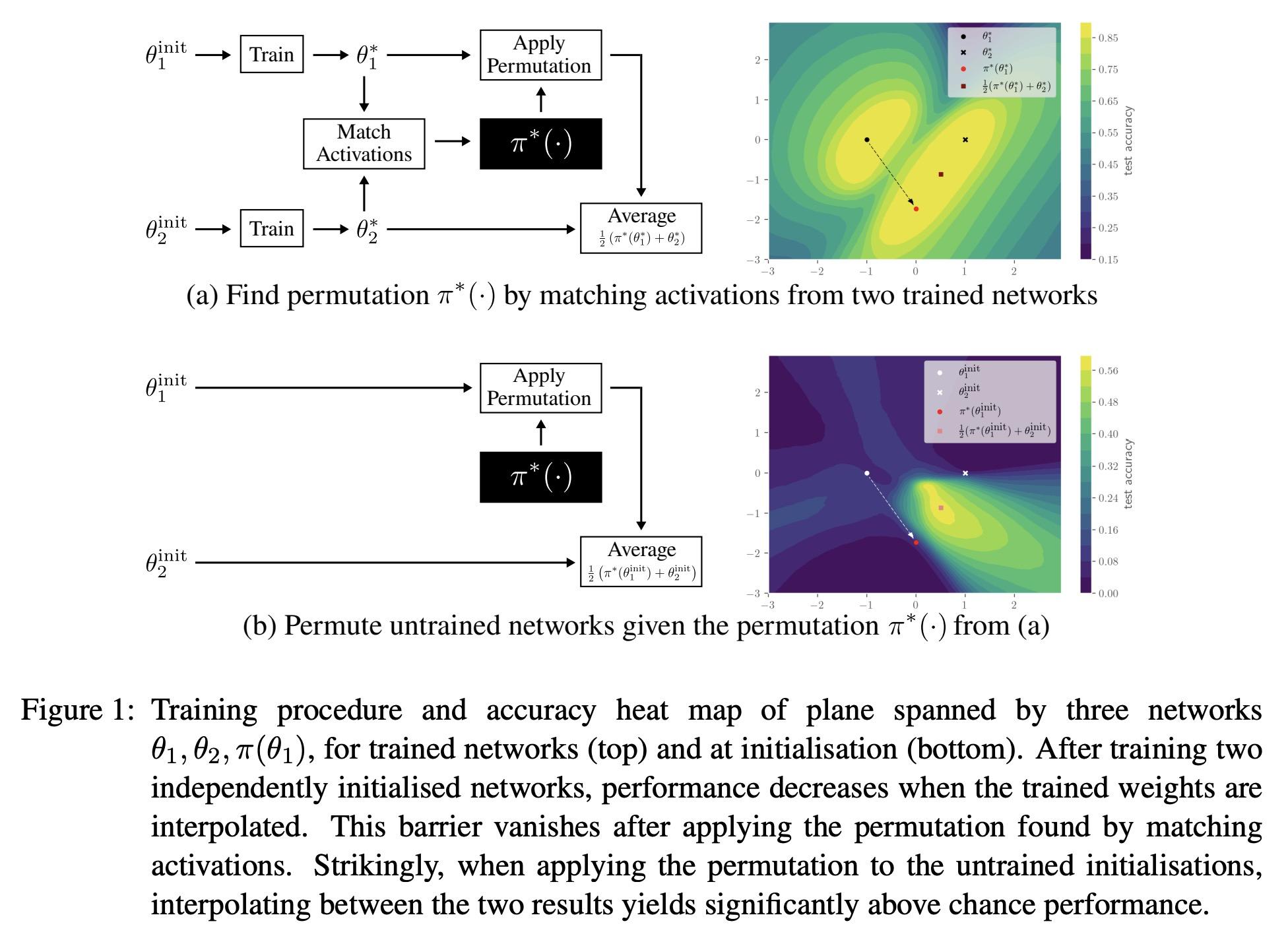
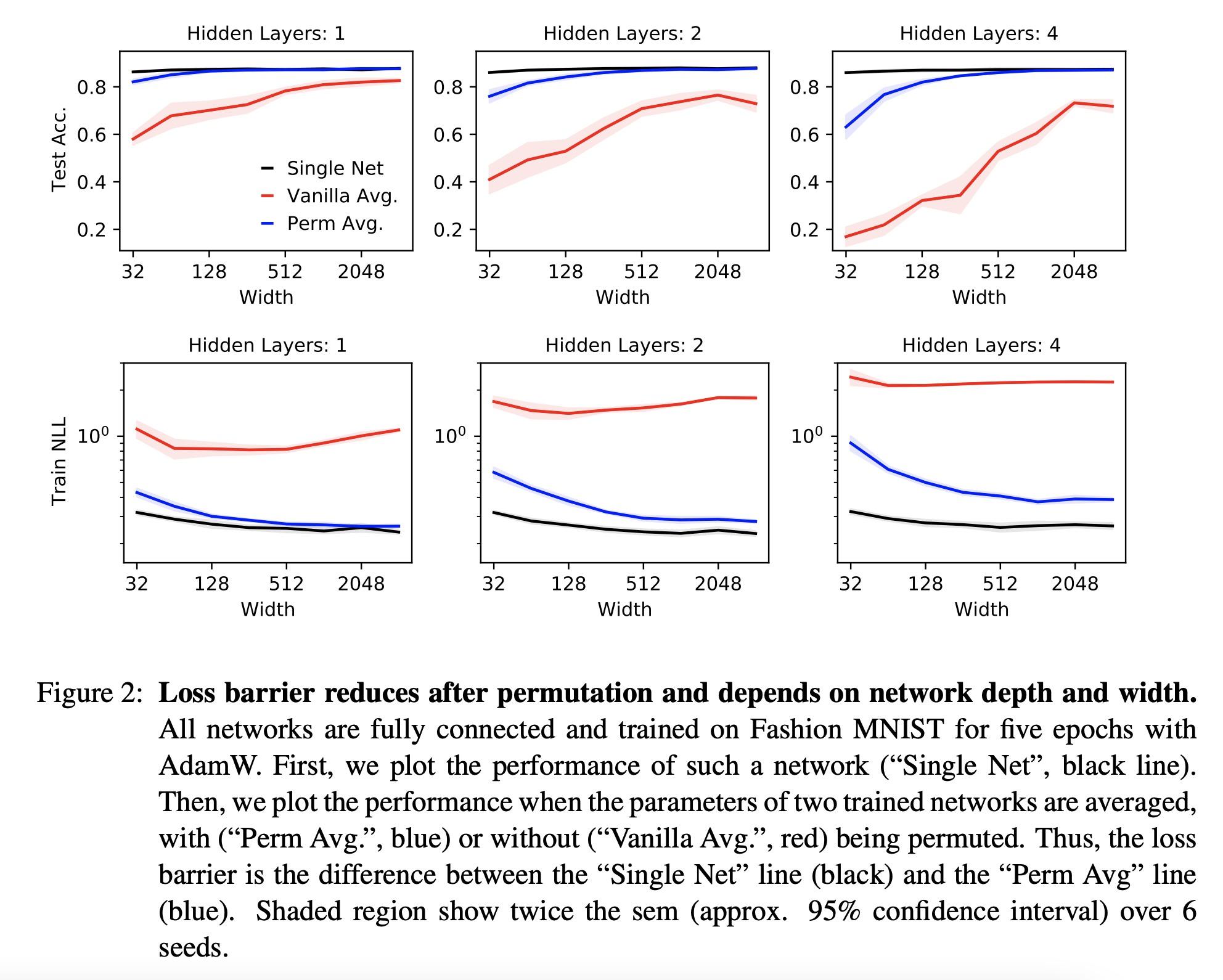
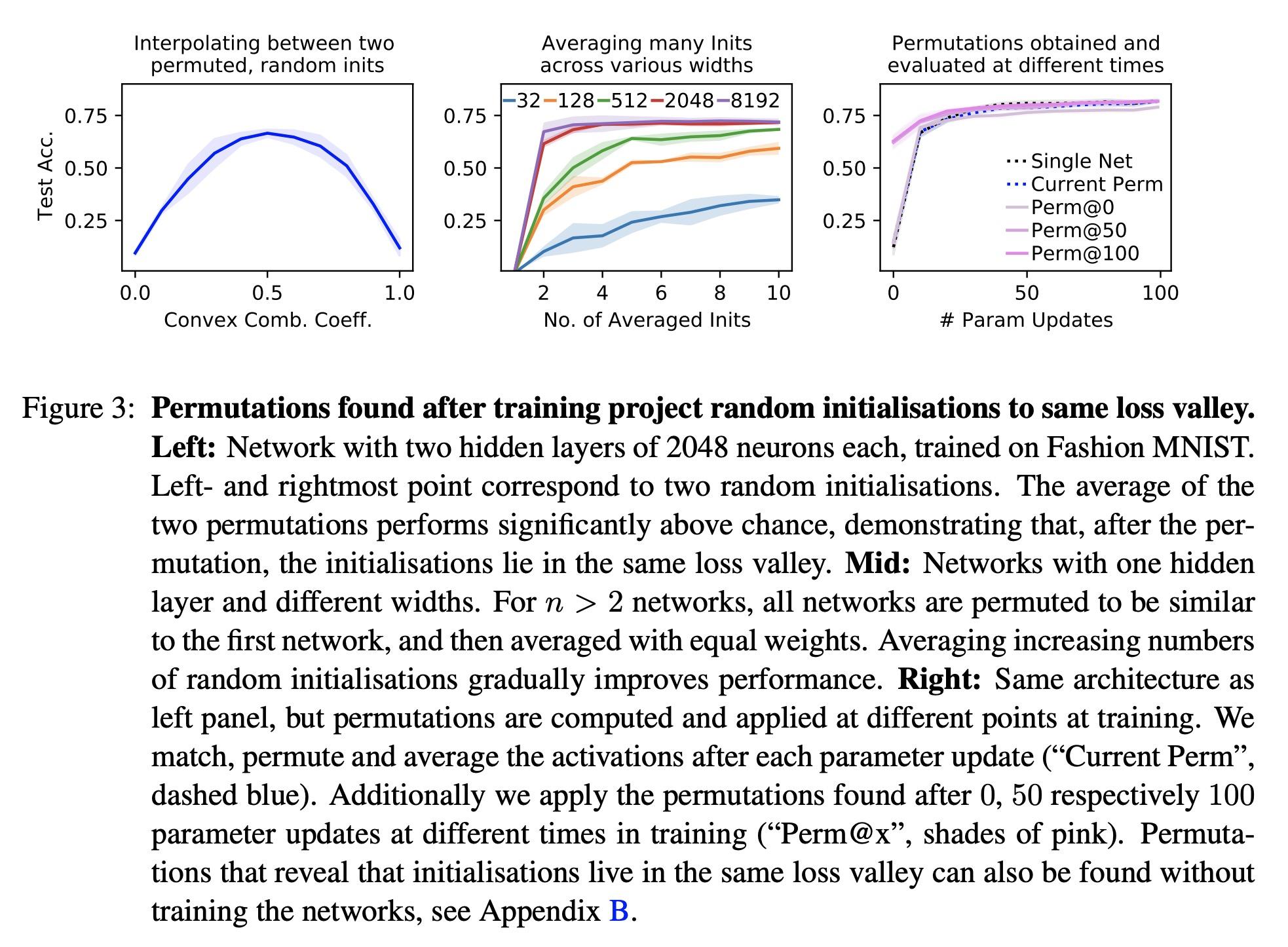
2、[LG] Random initialisations performing above chance and how to find them
F Benzing, S Schug, R Meier, J v Oswald, Y Akram, N Zucchet, L Aitchison, A Steger
[ETH Zurich & University of Bristol]
超偶然随机初始化表现及如何找到它们。用随机梯度下降(SGD)训练的神经网络从不同的随机初始化开始,通常会找到功能上非常相似的解决方案,这就提出了不同的SGD解决方案之间是否存在有意义的差异的问题。Entezari等人最近猜想,尽管初始化不同,但考虑到神经网络的互换不变性,SGD发现的解决方案位于相同的损失谷中。具体来说,他们假设通过SGD找到的任何两个解决方案都可以替换,使它们的参数之间的线性插值形成一条没有明显损失增加的路径。本文用一个简单而强大的算法来寻找这样的排列组合,能获得直接的经验证据,证明该假设在全连接网络中是真实的。令人震惊的是,本文发现两个网络在初始化时已经是在相同的损失谷中,而且其随机的、但经过适当排列的初始化的平均表现明显高于偶然性选择。相比之下,对于卷积架构,所得证据表明该假设并不成立。特别是在大学习率设置下,SGD似乎发现了不同的模式。
Neural networks trained with stochastic gradient descent (SGD) starting from different random initialisations typically find functionally very similar solutions, raising the question of whether there are meaningful differences between different SGD solutions. Entezari et al. recently conjectured that despite different initialisations, the solutions found by SGD lie in the same loss valley after taking into account the permutation invariance of neural networks. Concretely, they hypothesise that any two solutions found by SGD can be permuted such that the linear interpolation between their parameters forms a path without significant increases in loss. Here, we use a simple but powerful algorithm to find such permutations that allows us to obtain direct empirical evidence that the hypothesis is true in fully connected networks. Strikingly, we find that two networks already live in the same loss valley at the time of initialisation and averaging their random, but suitably permuted initialisation performs significantly above chance. In contrast, for convolutional architectures, our evidence suggests that the hypothesis does not hold. Especially in a large learning rate regime, SGD seems to discover diverse modes.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.07509

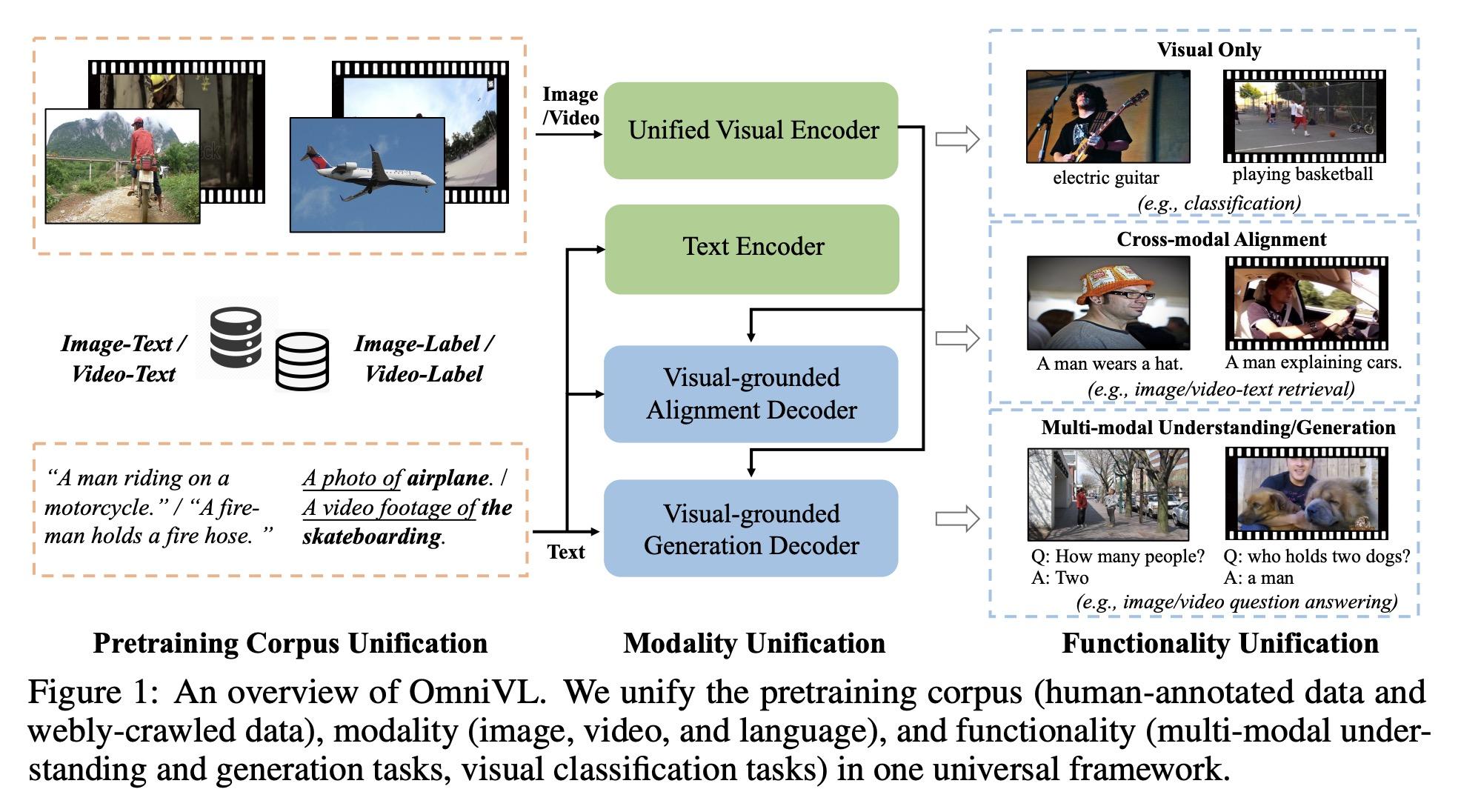
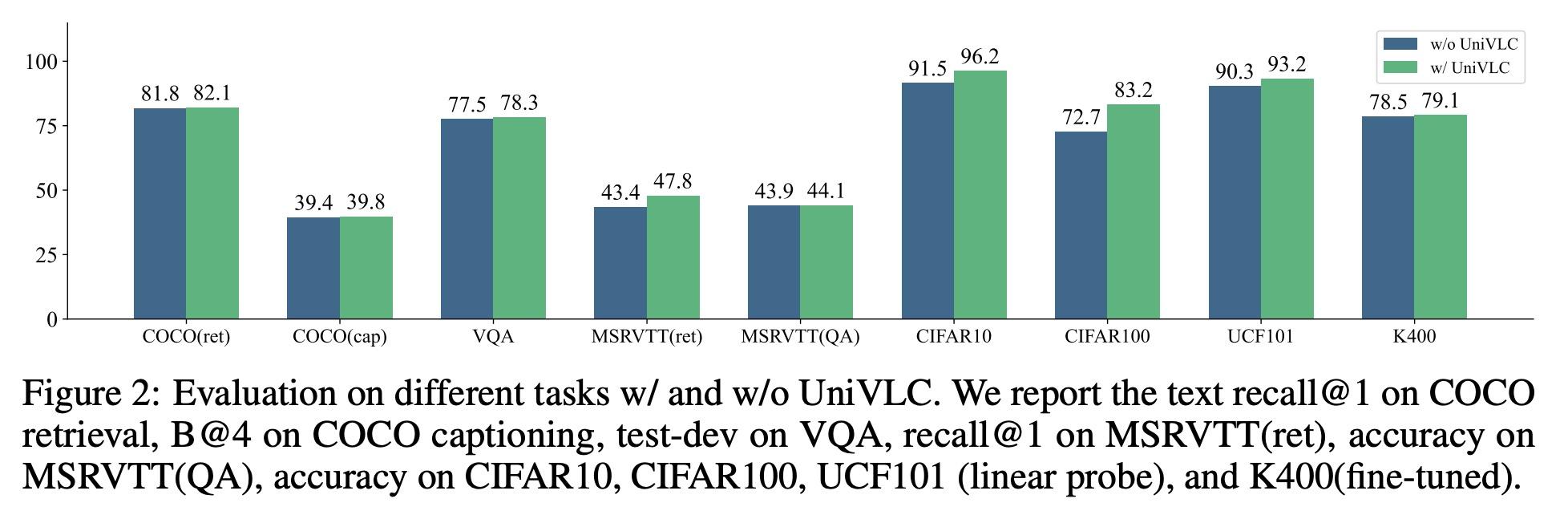
3、[CV] OmniVL:One Foundation Model for Image-Language and Video-Language Tasks
J Wang, D Chen, Z Wu, C Luo, L Zhou, Y Zhao, Y Xie, C Liu, Y Jiang, L Yuan
[Fudan University & Microsoft Cloud + AI & Microsoft Research Asia]
OmniVL:面向图像-语言和视频-语言任务的基础模型。本文提出OmniVL,一种新的基础模型,用一个通用架构支持图像-语言和视频-语言任务,为图像和视频输入采用统一的基于Transformer的视觉编码器,因此可以进行图像-语言和视频-语言的联合预训练。本文首次证明,这种范式对图像和视频任务都有好处,而不是传统的单向迁移(例如,用图像-语言来帮助视频-语言)。为此,本文提出一种图像-语言和视频-语言的解耦联合预训练,以有效地将视觉语言建模分解为空间和时间维度,并在图像和视频任务上获得性能提升。此外,本文还提出一种新的统一视觉-语言对比(UniVLC)损失,将图像-文本、视频-文本、图像-标签(如图像分类)、视频-标签(如视频动作识别)数据结合起来,从而尽可能地利用有监督和无监督的预训练数据。在不产生额外特定任务适配器的情况下,OmniVL可以同时支持只有视觉的任务(如图像分类、视频动作识别)、跨模态的对齐任务(如图像/视频-文本检索)以及多模态的理解和生成任务(如图像/视频问答、字幕)。在广泛的下游任务上对OmniVL进行了评估,并在相似的模型大小和数据规模下取得了最先进或有竞争力的结果。
This paper presents OmniVL, a new foundation model to support both imagelanguage and video-language tasks using one universal architecture. It adopts a unified transformer-based visual encoder for both image and video inputs, and thus can perform joint image-language and video-language pretraining. We demonstrate, for the first time, such a paradigm benefits both image and video tasks, as opposed to the conventional one-directional transfer (e.g., use image-language to help videolanguage). To this end, we propose a decoupled joint pretraining of image-language and video-language to effectively decompose the vision-language modeling into spatial and temporal dimensions and obtain performance boost on both image and video tasks. Moreover, we introduce a novel unified vision-language contrastive (UniVLC) loss to leverage image-text, video-text, image-label (e.g., image classification), video-label (e.g., video action recognition) data together, so that both supervised and noisily supervised pretraining data are utilized as much as possible. Without incurring extra task-specific adaptors, OmniVL can simultaneously support visual only tasks (e.g., image classification, video action recognition), cross-modal alignment tasks (e.g., image/video-text retrieval), and multi-modal understanding and generation tasks (e.g., image/video question answering, captioning). We evaluate OmniVL on a wide range of downstream tasks and achieve state-of-the-art or competitive results with similar model size and data scale.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.07526

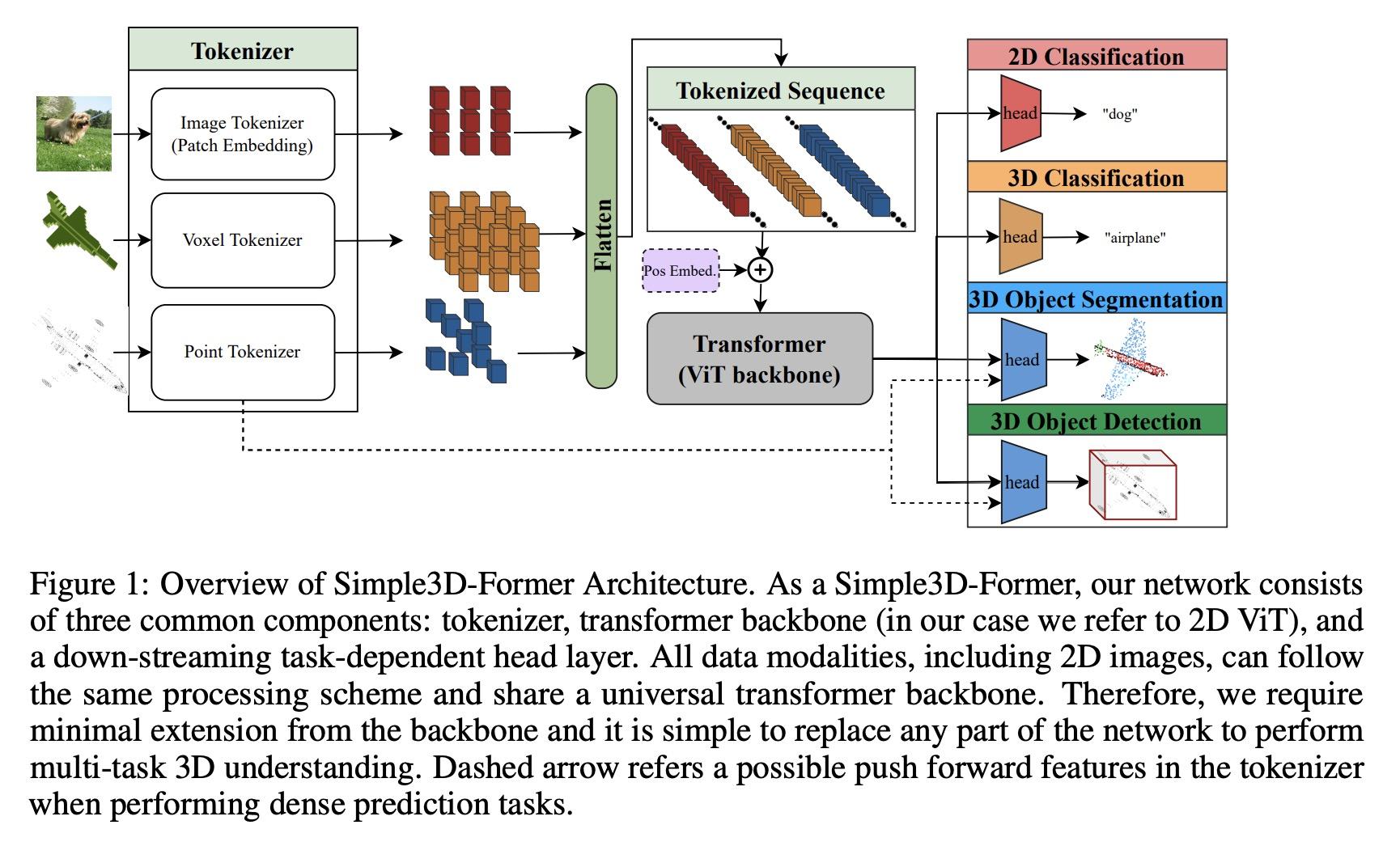
4、[CV] Can We Solve 3D Vision Tasks Starting from A 2D Vision Transformer?
Y Wang, Z Fan, T Chen, H Fan, Z Wang
[UT Austin & National University of Singapore]
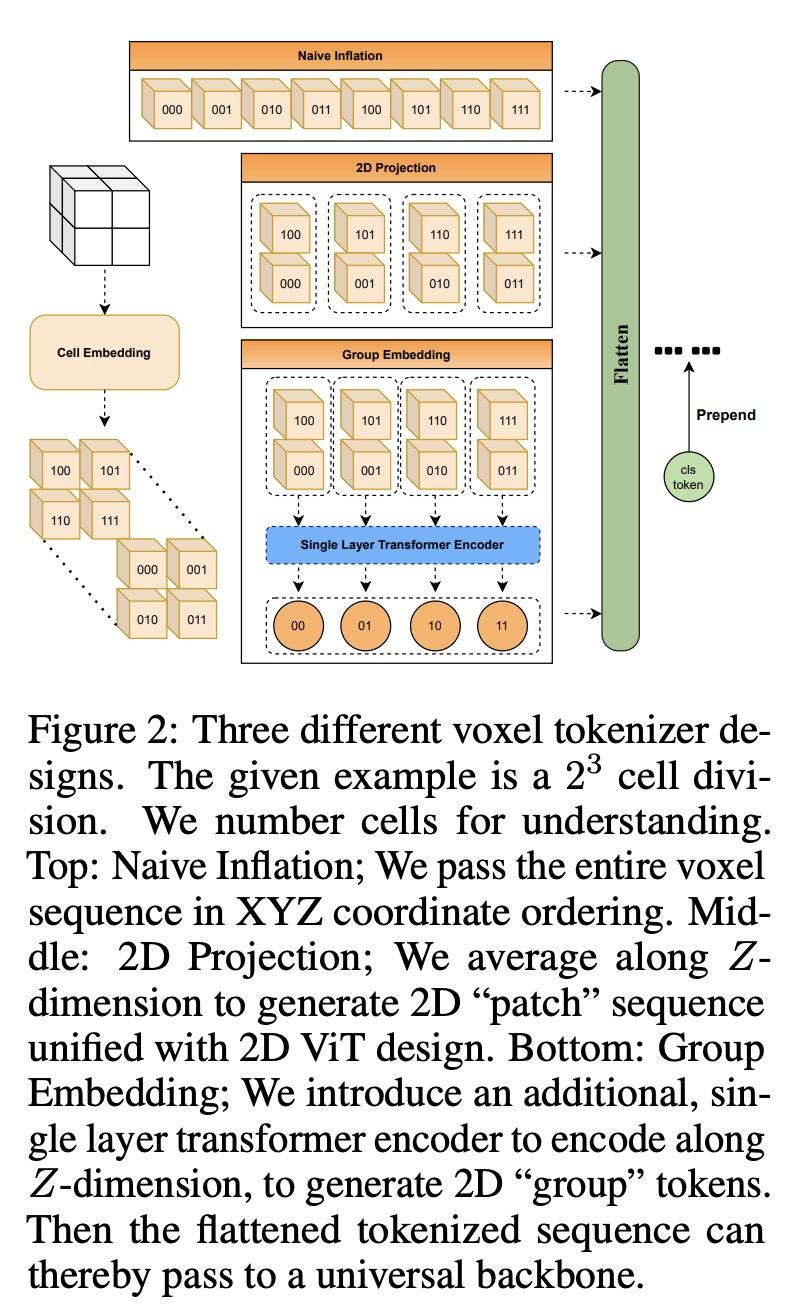
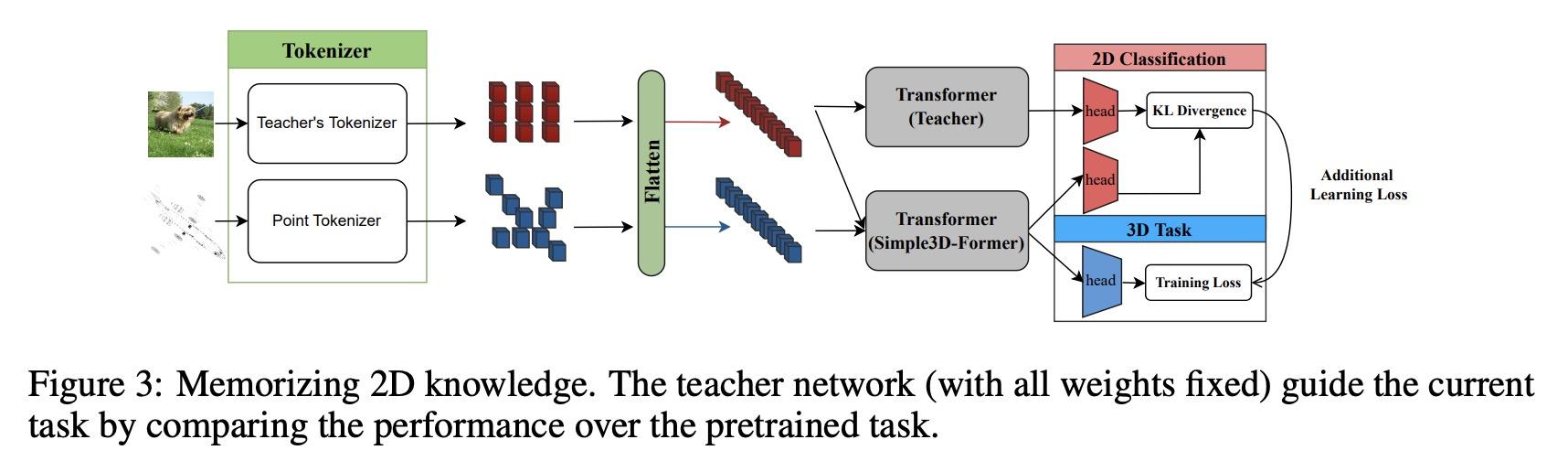
能从2D视觉Transformer开始解决3D视觉任务吗?视觉Transformer(ViT)已被证明是有效的,通过对大规模图像数据集的训练来解决2D图像理解任务;同时,作为一个独立的轨道,也可以对3D视觉世界进行建模,如体素或点云。然而,随着人们越来越希望Transformer能成为异质数据的"通用"建模工具,用于2D和3D任务的ViT到目前为止已经采用了截然不同的架构设计,几乎无法迁移。这就引出了一个(过于)雄心勃勃的问题:能否缩小2D和3D ViT架构之间的差距?作为一项试验性研究,本文展示了理解3D视觉世界的诱人前景,使用标准的2D ViT架构,只需在输入和输出层面进行最小的定制,而无需重新设计管道。为了从其2D模型中建立一个3D ViT,本文"膨胀"了图块嵌入和Token序列,同时还设计了新的位置编码机制以匹配3D数据的几何结构。由此产生的"极简"3D ViT称为Simple3D-Former,与高度定制的3D特定设计相比,在流行的3D任务(如目标分类、点云分割和室内场景检测)上的表现令人惊讶地强大。因此,它可以作为新的3D ViT的一个强有力的基线。此外,本文注意到,追求一个统一的2D-3D ViT设计,除了科学上的好奇心,还有实际意义。具体来说,本文证明了Simple3D-Former能够自然地利用来自大规模现实2D图像(如ImageNet)的大量预训练权重,这些权重可以"零成本"插入以提高3D任务性能。
Vision Transformers (ViTs) have proven to be effective, in solving 2D image understanding tasks by training over large-scale image datasets; and meanwhile as a somehow separate track, in modeling the 3D visual world too such as voxels or point clouds. However, with the growing hope that transformers can become the “universal” modeling tool for heterogeneous data, ViTs for 2D and 3D tasks have so far adopted vastly different architecture designs that are hardly transferable. That invites an (over-)ambitious question: can we close the gap between the 2D and 3D ViT architectures? As a piloting study, this paper demonstrates the appealing promise to understand the 3D visual world, using a standard 2D ViT architecture, with only minimal customization at the input and output levels without redesigning the pipeline. To build a 3D ViT from its 2D sibling, we “inflate” the patch embedding and token sequence, accompanied with new positional encoding mechanisms designed to match the 3D data geometry. The resultant “minimalist” 3D ViT, named Simple3D-Former, performs surprisingly robustly on popular 3D tasks such as object classification, point cloud segmentation and indoor scene detection, compared to highly customized 3D-specific designs. It can hence act as a strong baseline for new 3D ViTs. Moreover, we note that pursing a unified 2D-3D ViT design has practical relevance besides just scientific curiosity. Specifically, we demonstrate that Simple3D-Former naturally enables to exploit the wealth of pre-trained weights from large-scale realistic 2D images (e.g., ImageNet), which can be plugged in to enhancing the 3D task performance “for free”. Our code is available at https://github.com/Reimilia/Simple3D-Former.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.07026

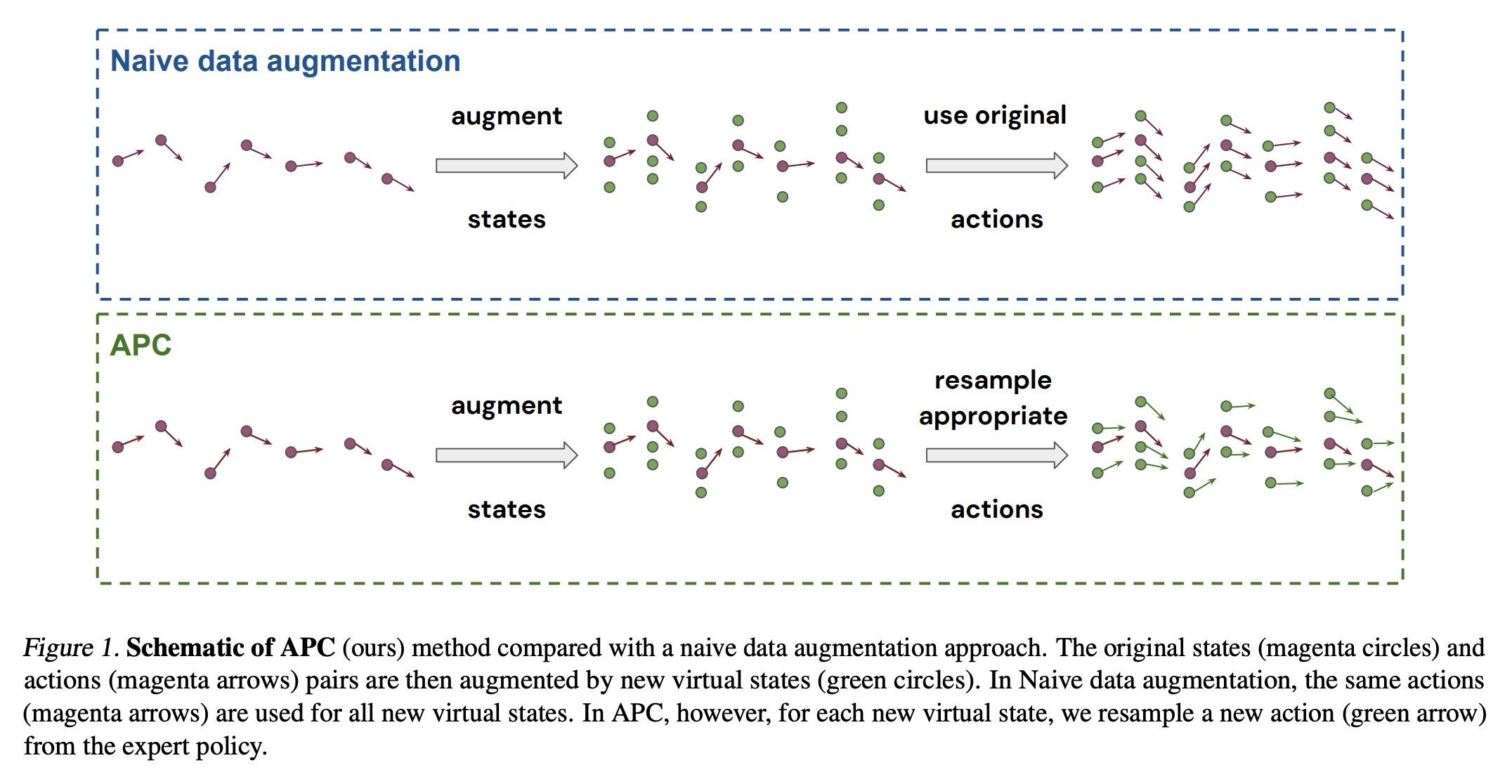
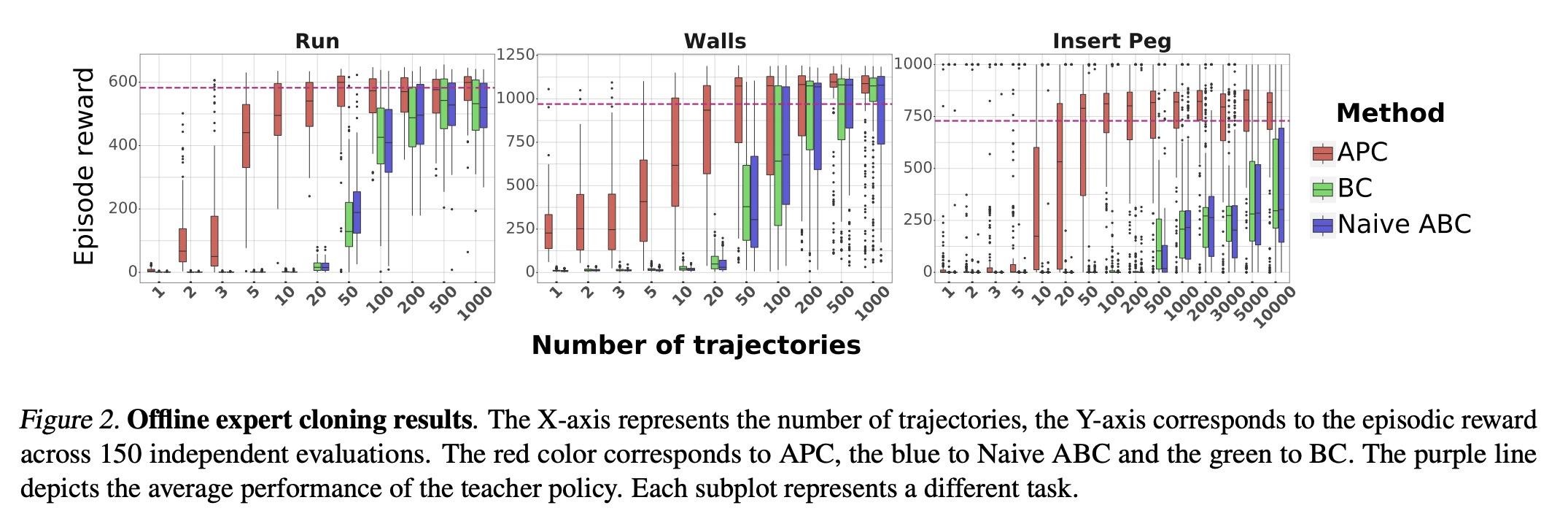
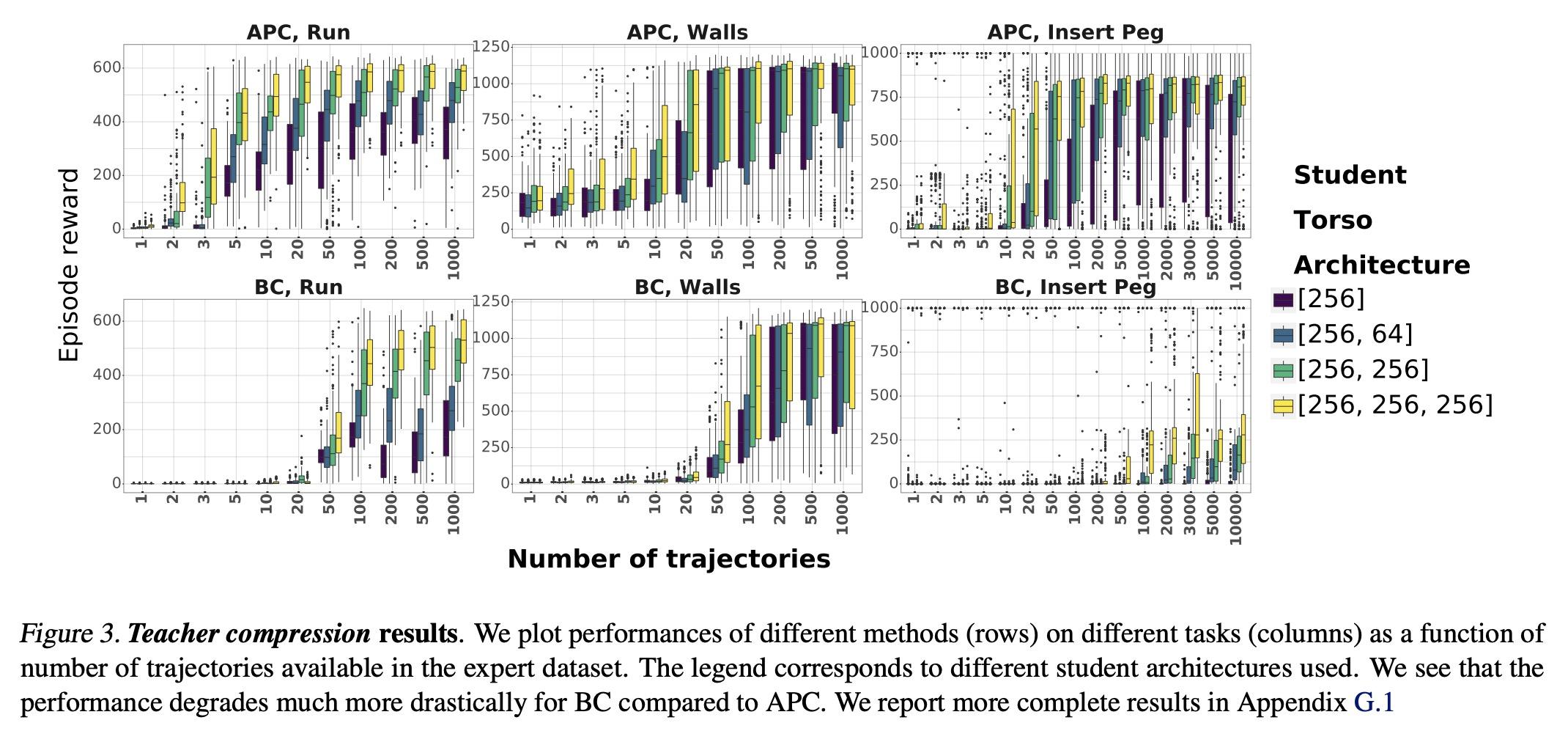
5、[LG] Data augmentation for efficient learning from parametric experts
A Galashov, J Merel, N Heess
[DeepMind]
基于参数化专家的高效学习数据增强。本文提出一种简单而有效的数据增强技术,以实现从参数化专家那里高效地学习强化学习和模仿学习的数据。本文专注于所说的策略克隆设置,用专家或专家策略的在线或离线查询来告知学生策略的行为。这种设置自然地出现在一些问题中,例如作为行为克隆的变体,或作为其他算法的组成部分,如DAGGER、策略蒸馏或KL-regularized RL。所提出的方法,即增强策略克隆(APC),用合成状态来诱导采样轨迹周围区域的反馈敏感性,从而极大减少了成功克隆专家所需的环境交互作用。对于高自由度的控制问题,实现了从专家到学生策略的高度数据效率的行为迁移。在几个现有的和广泛使用的算法的背景下证明了所提出方法的好处,这些算法包括策略克隆作为一个组成部份。此外,本文强调了该方法在两个实际相关的环境中的好处(a)专家压缩,即用更少的参数迁移到学生身上;以及(b)从有特权的专家那里迁移,即专家有一个与学生不同的观察空间,通常包括对特权信息的访问。
We present a simple, yet effective dataaugmentation technique to enable data-efficient learning from parametric experts for reinforcement and imitation learning. We focus on what we call the policy cloning setting, in which we use online or offline queries of an expert or expert policy to inform the behavior of a student policy. This setting arises naturally in a number of problems, for instance as variants of behavior cloning, or as a component of other algorithms such as DAGGER, policy distillation or KL-regularized RL. Our approach, augmented policy cloning (APC), uses synthetic states to induce feedback-sensitivity in a region around sampled trajectories, thus dramatically reducing the environment interactions required for successful cloning of the expert. We achieve highly data-efficient transfer of behavior from an expert to a student policy for highdegrees-of-freedom control problems. We demonstrate the benefit of our method in the context of several existing and widely used algorithms that include policy cloning as a constituent part. Moreover, we highlight the benefits of our approach in two practically relevant settings (a) expert compression, i.e. transfer to a student with fewer parameters; and (b) transfer from privileged experts, i.e. where the expert has a different observation space than the student, usually including access to privileged information.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.11448

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
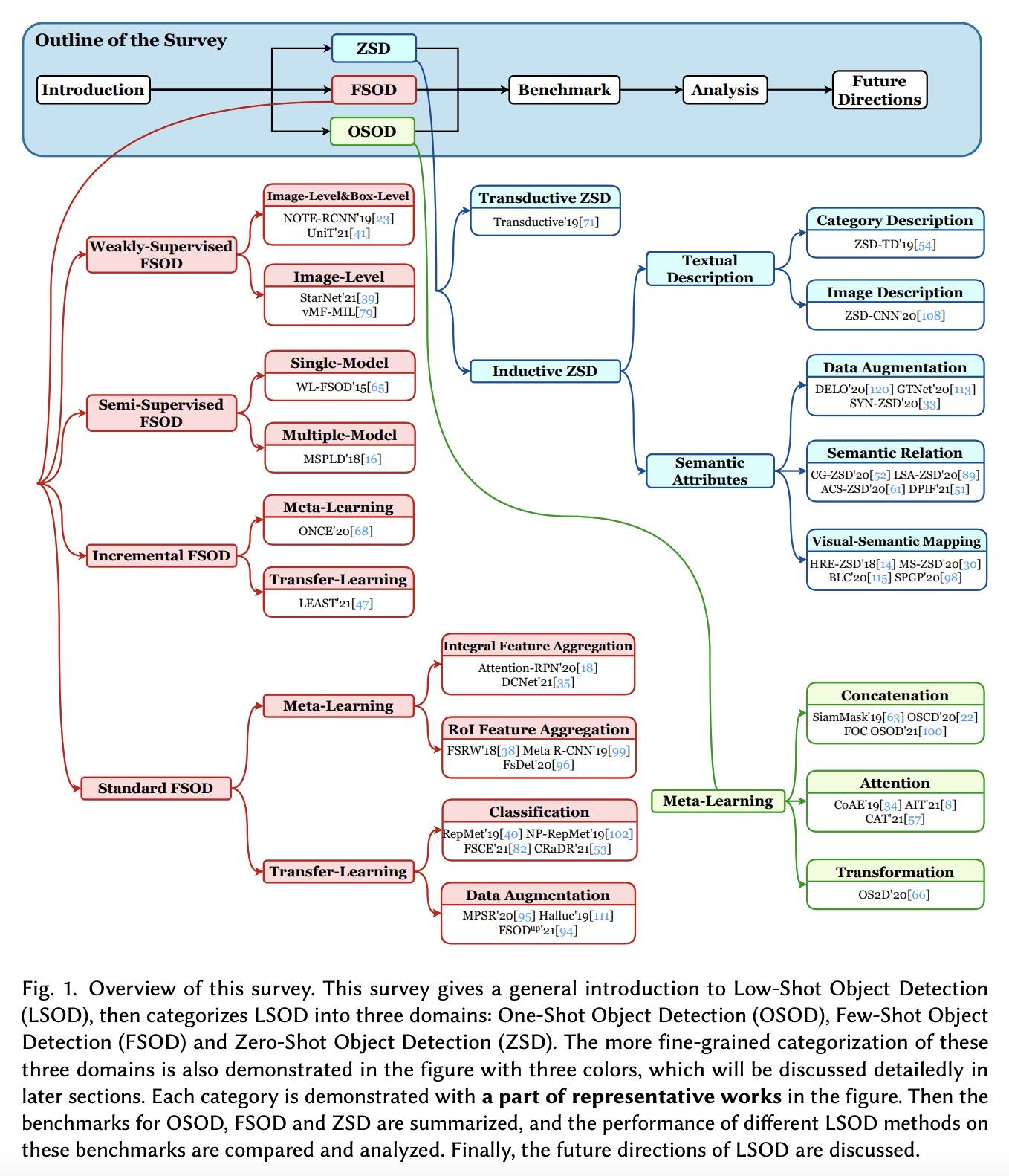
[CV] A Survey of Deep Learning for Low-Shot Object Detection
深度学习低样本目标检测综述
Q Huang, H Zhang, M Xue, J Song, M Song
[Zhejiang University]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.02814

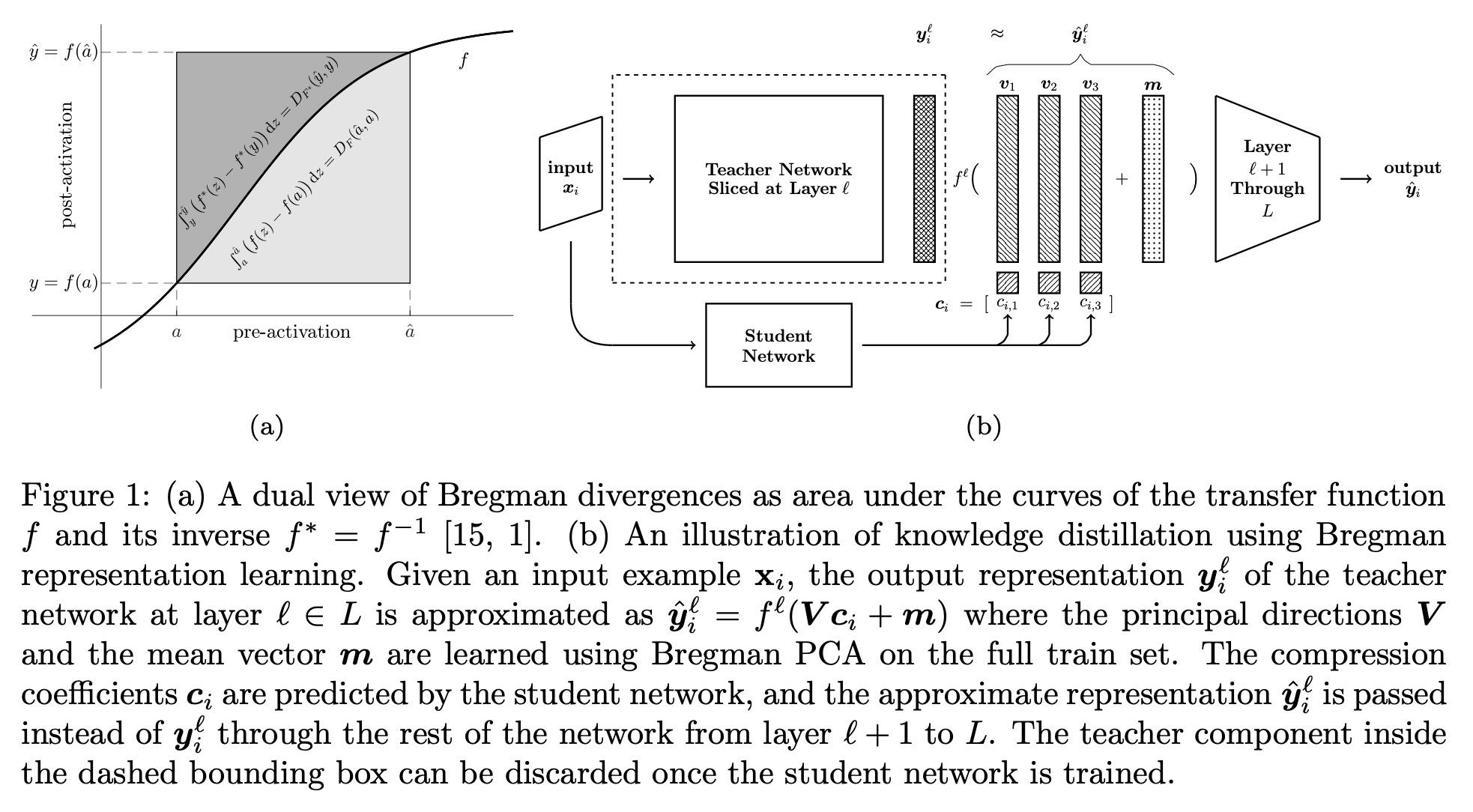
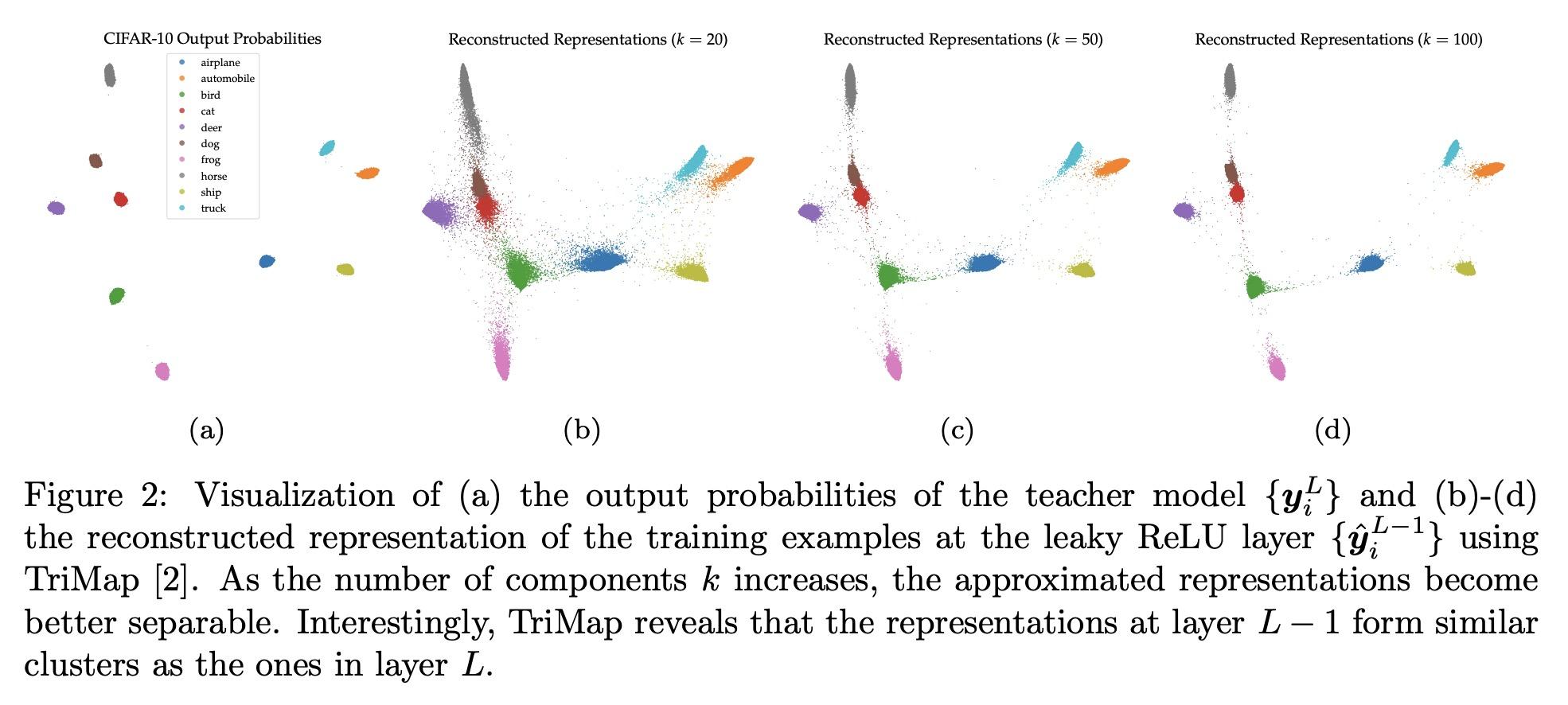
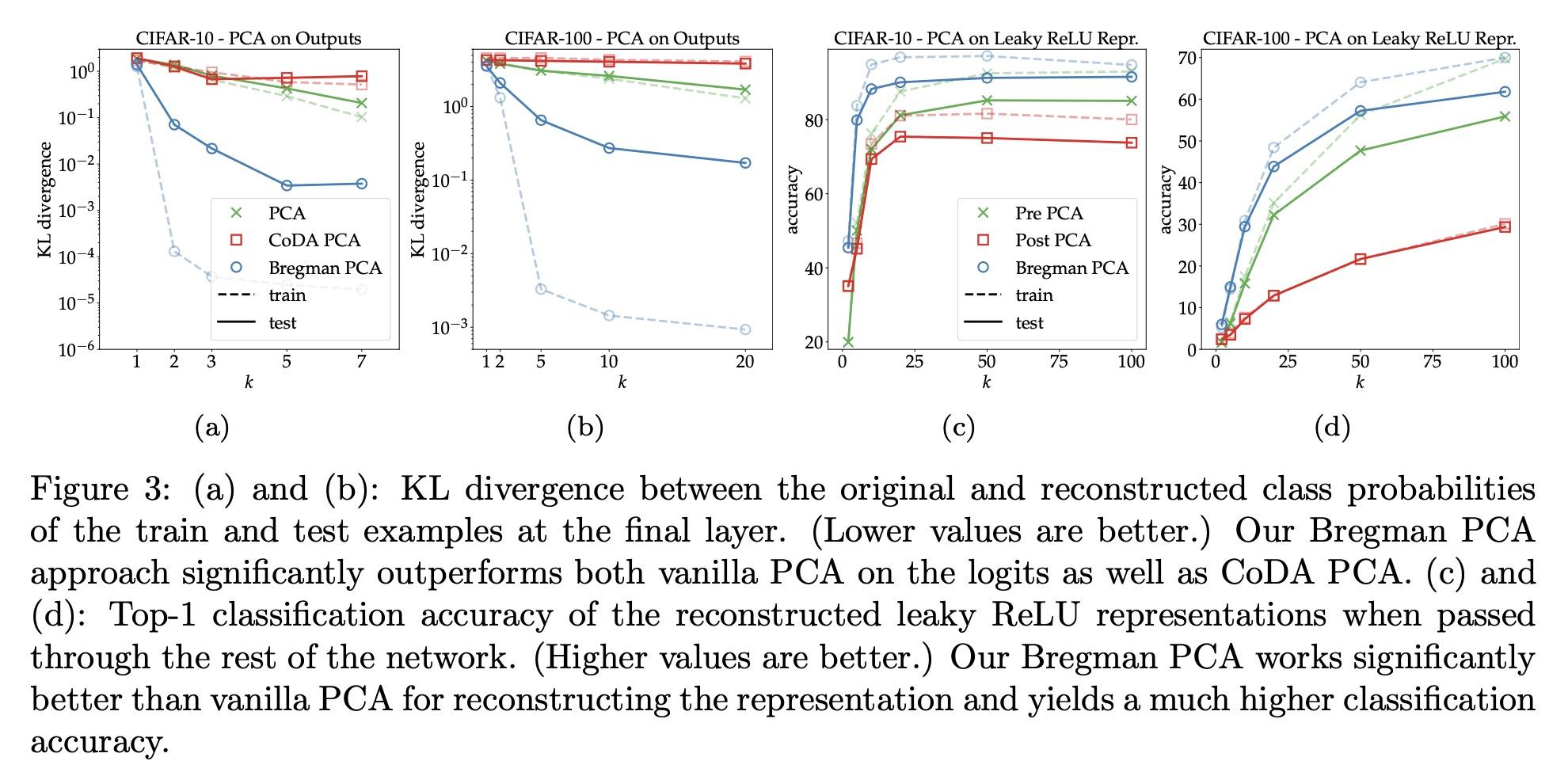
[LG] Layerwise Bregman Representation Learning with Applications to Knowledge Distillation
分层Bregman表示学习及其知识蒸馏应用
E Amid, R Anil, C Fifty, M K. Warmuth
[Google Research]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.07080

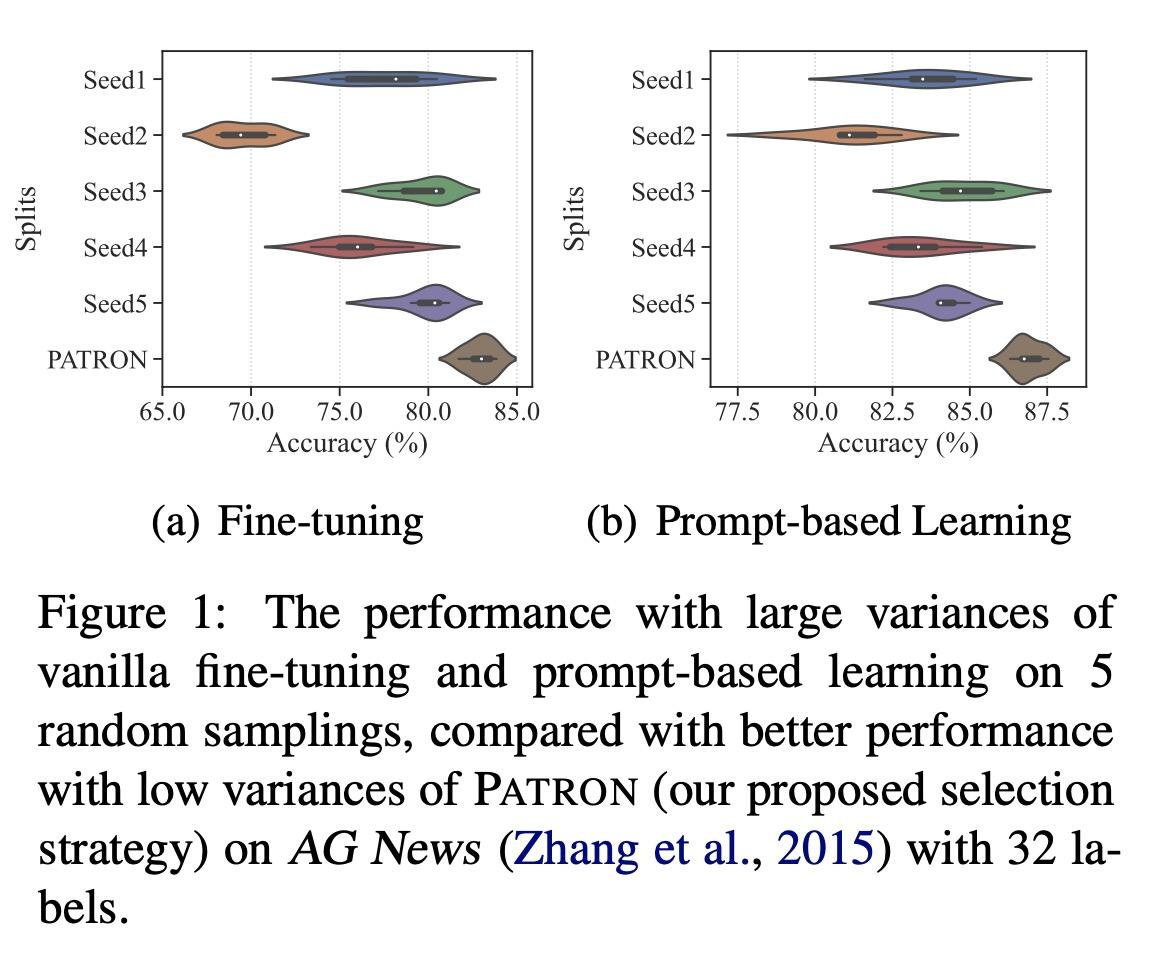
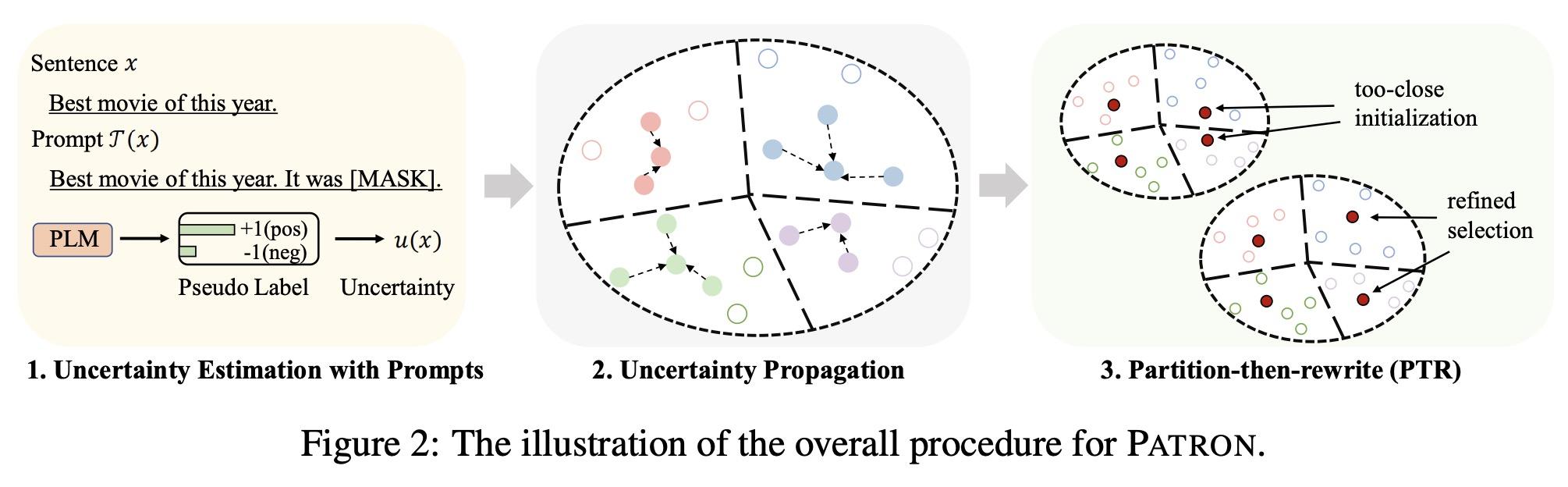
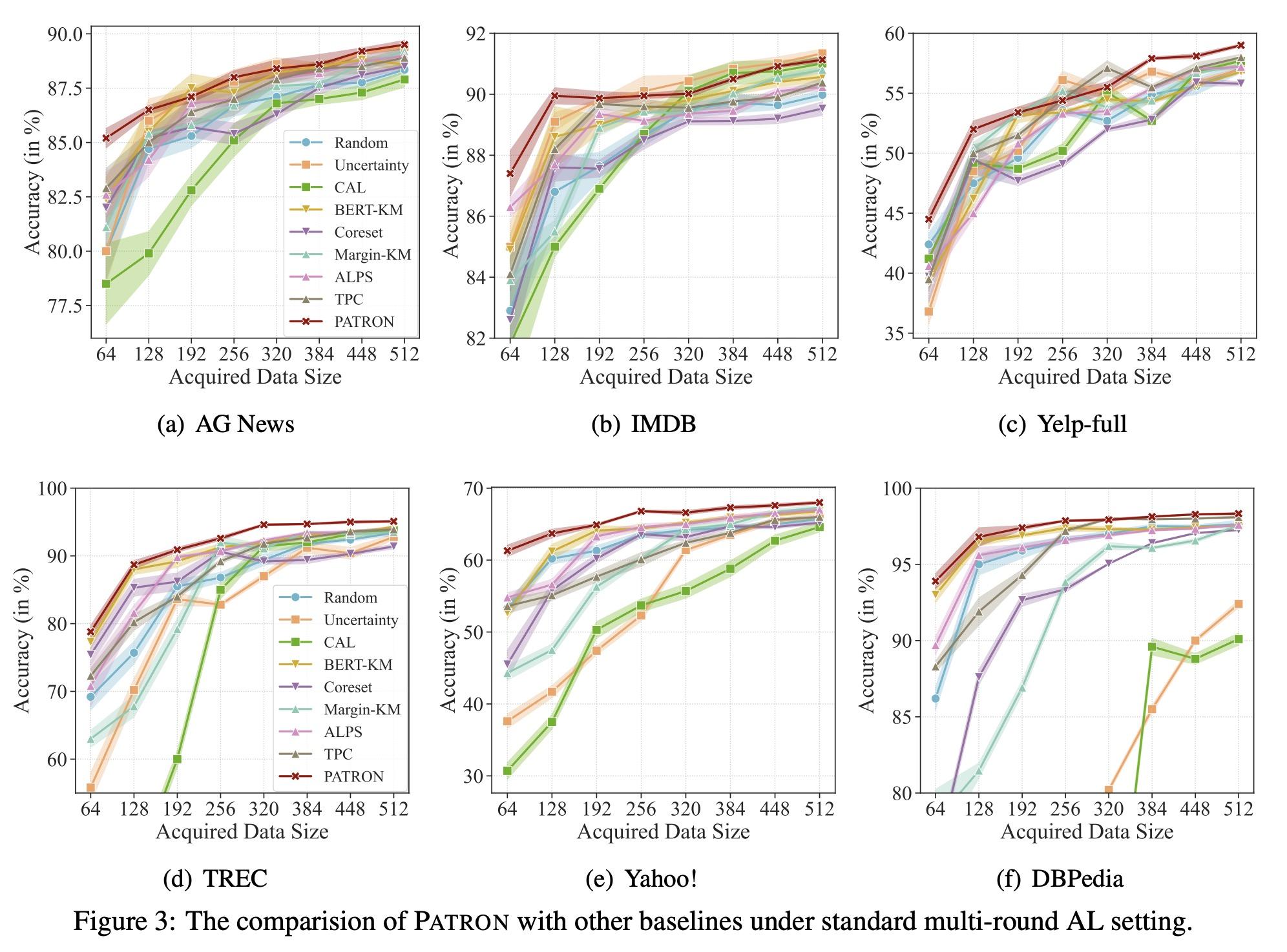
[CL] Cold-Start Data Selection for Few-shot Language Model Fine-tuning: A Prompt-Based Uncertainty Propagation Approach
少样本语言模型微调的冷启动数据选择:一种基于提示的不确定性传播方法
Y Yu, R Zhang...
[Georgia Institute of Technology & University of Washington & Google]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.06995

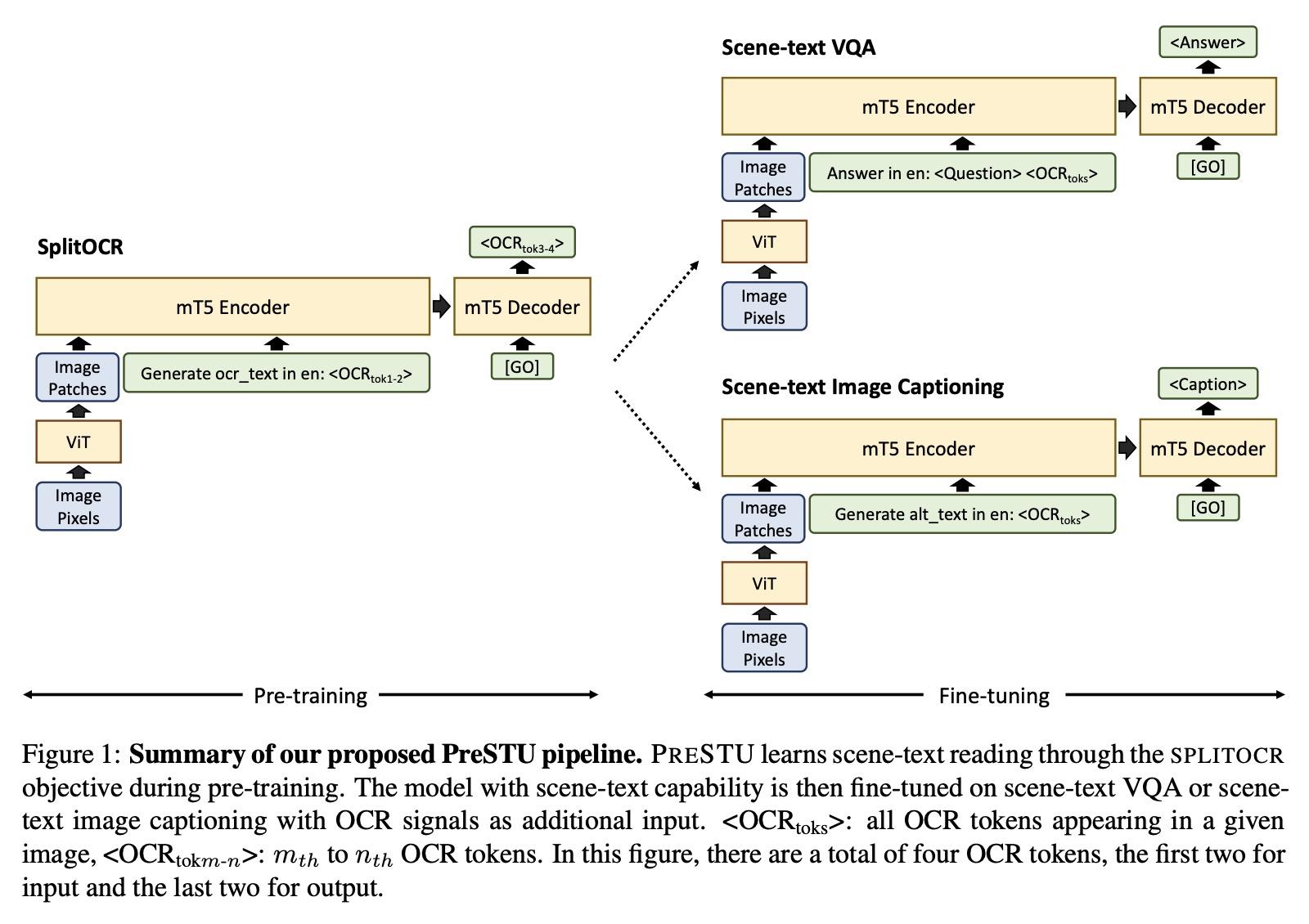
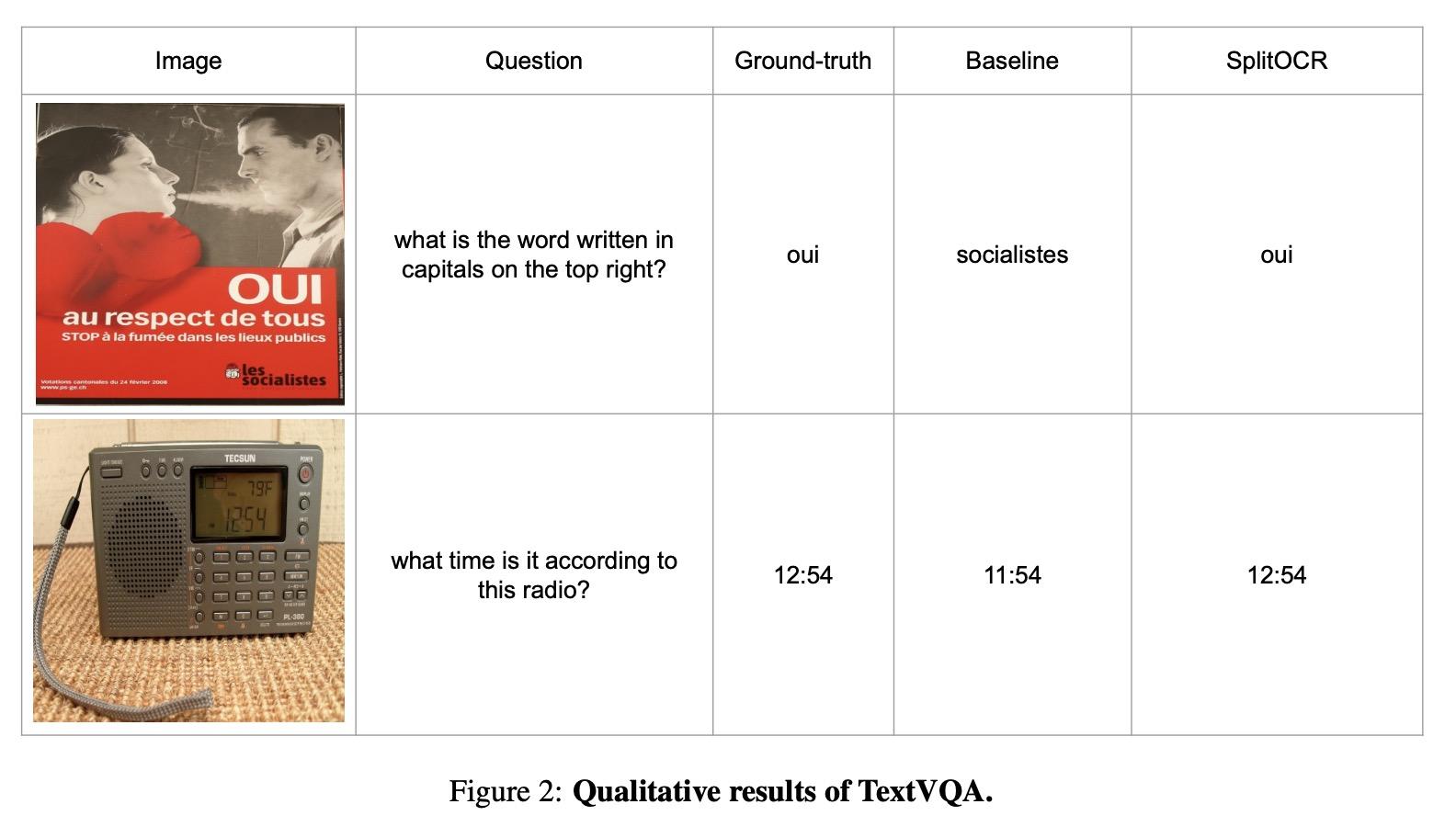
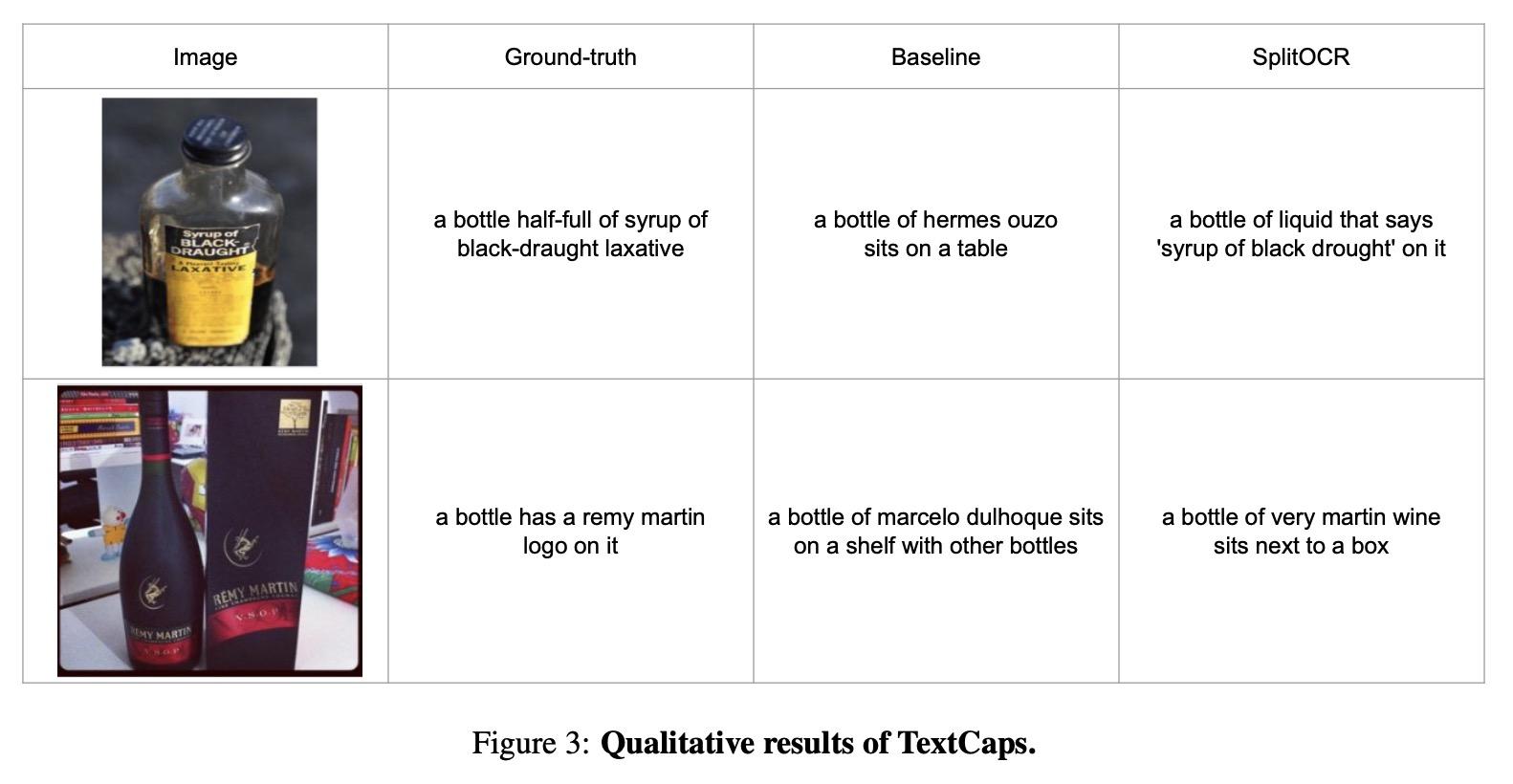
[CV] PreSTU: Pre-Training for Scene-Text Understanding
PreSTU:场景文本理解预训练
J Kil, S Changpinyo, X Chen, H Hu, S Goodman, W Chao, R Soricut
[The Ohio State University & Google Research]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.05534

 |
|